How to Get Started with Forex Trading: A Beginner’s Step-by-Step Guide
In today’s interconnected world, the financial markets have become more accessible to individuals from all walks of life. One such market that has gained immense popularity in recent years is the foreign exchange market, commonly known as Forex. Forex Trading offers opportunities to profit from the variations in currency exchange rates. This article explains Forex Trading in simple terms so that anyone can understand it, even with a basic education.
Chapter 1: Understanding Forex Trading
What is Forex?
Forex, short for “foreign exchange,” is the global marketplace for buying and selling currencies. It’s the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. Unlike stock markets, Forex Trading operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, owing to its decentralized nature.
Currency Pairs
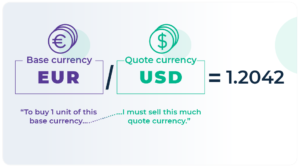
In Forex Trading, currency pairs are the foundation of the foreign exchange (Forex) market. They represent the relative value of one currency against another. In Forex trading, we quote currencies in pairs, and each pair comprises a base currency and a counter currency.
For instance, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro (EUR) is the base currency, and the US dollar (USD) is the counter currency. The exchange rate tells you how much of the counter currency you need to buy one unit of the base currency.
We categorize currency pairs into three groups:
Major, minor, and exotic. Major pairs involve the world’s most powerful currencies,
Such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD. Minor pairs don’t include the US dollar but still have global significance, like EUR/GBP. Exotic pairs comprise one major currency and one from a smaller or emerging economy, like USD/TRY.
Traders analyze currency pairs to speculate on price movements. If they believe the base currency will strengthen against the counter currency, they buy the pair (go long). Conversely, if they expect the base currency to weaken, they sell the pair (go short).
Chapter 2: How Forex Trading Works

Market Participants
Forex Trading is a market where banks, institutions, governments, corporations, and traders buy and sell currencies. Individual traders like you and me take part through brokers who act as mediators.
Leverage
In simple terms, leverage in forex trading allows you to control a larger position size with a relatively smaller amount of capital. It’s like borrowing money from your broker to trade larger positions than you could with just your own money.
Let’s break it down further:
Imagine you have $1,000 in your trading account, and you want to trade the EUR/USD currency pair. Without leverage, you could only control a position size of $1,000 worth of EUR/USD.
However, with leverage, your broker might offer you a leverage ratio of 50:1. This means for every $1 in your account, you can control a trade worth $50. So, with your $1,000 and 50:1 leverage, you can trade a position size of $50,000 worth of EUR/USD.
Real-life Example
Let’s illustrate the impact of leverage with a real-life example:
Trader A and Trader B both have $1,000 in their trading accounts.
Trader A use no leverage and opens a position with their entire $1,000 on the EUR/USD pair.
Trader B uses 50:1 leverage and opens a position worth $50,000 on the same currency pair.
Scenario 1: The EUR/USD pair moves in favor of both traders by 2%.
Trader A’s profit: $1,000 x 2% = $20
Trader B’s profit: $50,000 x 2% = $1,000
In this scenario, Trader B, who used leverage, made a more substantial profit compared to Trader A.
Scenario 2: The EUR/USD pair moves against both traders by 2%.
Trader A’s loss: $1,000 x 2% = $20
Trader B’s loss: $50,000 x 2% = $1,000
However, in this scenario, Trader B also incurs a more significant loss due to the leverage used.
Understanding the Benefits and risks of leverage in Forex
What is forex pips and How to Calculate?

A Forex pip calculator is a tool used to calculate the value of a pip in a currency pair. Here’s a simple formula to calculate pip value:
Pip Value = (Pip in decimal places / Current exchange rate) * Trade size
For example, if you’re trading EUR/USD with a pip value of 0.0001 and your trade size is 10,000 units,
Pip Value = (0.0001 / Current exchange rate) * 10,000


You can find the current exchange rate on your trading platform or through various financial websites. Plug in the values and calculate to determine the pip value for your specific trade.
Forex Pips–An Easy Guide to Counting
Chapter 3: Getting Started in Forex Trading
Education and Research
Before diving into Forex Trading, it’s crucial to educate yourself. Start with understanding basic trading concepts, like technical and fundamental analysis. Many educational resources are available for free online, such as videos, ebooks, and courses.
Selecting a Reliable Broker
Choosing the right Forex broker. Look for a broker with an excellent reputation, competitive spreads (the difference between the bid and ask price), and regulatory compliance. It’s very essential to do thorough research and read reviews before opening an account.
Setting Up a Forex Trading Account
Once you’ve chosen a broker, you’ll need to open a Forex Trading Account. To complete this process, you need to give personal information, verify your identity, and add money to your account.
Chapter 4: Analyzing the Forex Market
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying historical price charts and patterns to make trading decisions. To predict future price changes, it uses indicators such as moving averages, RSI, and MACD.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on economic, and geopolitical factors that can influence currency exchange rates. Traders who use fundamental analysis keep attention on economic indicators, central bank policies, and news events.
Chapter 5: Making Your First Trade
Placing Orders
In Forex Trading, you can place original orders, such as market orders (buy or sell at the current market price) and limit orders (buy or sell at a specific price). Learning how to place orders correctly is essential for executing trades effectively.
Risk Management
Forex Trading, or foreign exchange trading, is a popular way to potentially make money by trading currencies. But, like any investment, it carries risks. To protect your hard-earned cash, it’s crucial to understand and practice good risk management.
Chapter 6: Common Mistakes to Avoid in Forex Trading

Overtrading
One common mistake among beginners is over-trading, which means making too many trades in a short period. This can lead to significant losses because of impulsive decisions.
Ignoring Risk Management
Failing to implement proper risk management strategies can wipe out your trading account quickly. Always use stop-loss orders and never risk more than you can afford to lose.
Lack of Patience
Forex Trading requires patience and discipline. It’s essential to wait for suitable trading opportunities and not rush into trades based on emotions.
Chapter 7: The Importance of Practice
Demo Forex Trading
Before risking real money, it’s highly recommended practicing with a demo trading account. You can use Demo Accounts to learn Forex Trading in your real money.
Trading Plan
Developing a trading plan is crucial. This plan should outline your trading strategy, risk tolerance, and goals. Stick to your plan to avoid making impulsive decisions.
Chapter 8: The Road to Success
Continuous Learning
Forex Trading is a growing field, and successful traders never stop learning. Stay updated with market news, attend webinars, and adapt your strategies to changing market conditions.
Emotional Control
Emotions can cloud judgment and lead to poor trading decisions. Successful traders remain calm and rational, even in the face of losses.
Chapter 9: Pros and Cons of Forex Trading

Pros of Trading Forex:
Accessibility: Forex markets are open 24 hours a day, five days a week, making it accessible to traders from around the world. This flexibility allows individuals to trade at their convenience.
Liquidity: The Forex market is one of the most liquid markets globally, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. Traders can enter and exit positions easily because of liquidity without causing big price fluctuations.
Leverage: Forex brokers offer high leverage, allowing traders to control large positions with relatively small amounts of capital. While this can amplify profits, it also increases the potential for losses, so it must be used cautiously.
Diverse Trading Opportunities: Traders can choose from a wide range of currency pairs to trade, including major, minor, and exotic pairs. This variety allows for different trading strategies and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
Low Transaction Costs: Forex trading typical Forex brokers offers high leverage, so traders can control large positions with little capital. spreads (the difference between the bid and ask prices) and, sometimes, commissions.
Technical Analysis: we know Forex markets for responding to technical analysis, making it appealing to traders who use charts, patterns, and indicators to make trading decisions.
Risk Management Tools: Forex traders have access to various risk management tools, including stop-loss and take-profit orders, which help control potential losses and secure profits automatically.
Cons of Trading Forex:
High Risk: Forex trading is highly speculative and involves a significant level of risk. Leverage can magnify both gains and losses, and it’s not uncommon for traders to lose their entire capital if they make poor decisions.
Complexity: Forex trading can be complex, especially for beginners. Understanding factors that influence exchange rates, such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, and central bank policies, requires in-depth knowledge and analysis.
Emotional Challenges: The fast-paced nature of Forex trading can lead to emotional challenges, including anxiety and stress. Emotional decision-making often results in poor trading outcomes.
Market Volatility: While liquidity can be an advantage, it can also lead to rapid and unpredictable price movements. Sudden news events or geopolitical developments can cause significant market volatility.
Broker Risks: Choosing the right Forex broker is crucial. Some brokers may engage in unethical practices or have inadequate security measures. It’s essential to research and select a reputable broker.
Over trading: Given the accessibility and availability of Forex markets, some traders may be tempted to over-trade, leading to excessive risk exposure and potential losses.
Learning Curve: Success in Forex trading requires a steep learning curve. Traders need to continually educate themselves and develop effective strategies to remain profitable.
Conclusion
You can develop both financially and personally through forex trading. While it may seem complex at first, with the right education, practices demo accounts to practice Forex Trading without risking your money.o, if you’re considering entering the world of Forex, start your journey with education, practice, and a well-thought-out trading plan. With time and dedication, you may find success in this exciting and dynamic market.